Porcelain Dental Veneers
All on 4 implants in Turkey
Porcelain Dental Veneers
Are your teeth discoloured, deformed, or have other aesthetic problems? If you are looking for an effective treatment method to solve these problems and care about the minimally invasive nature of the treatment and long-term results, we recommend that you read this article carefully.
Because in this article, we will talk about porcelain dental veneers. Ceramic dental veneers are an effective, reliable, and conservative method to improve dental aesthetics. Thanks to their natural appearance, durability, and biocompatibility, they will meet both your aesthetic and functional expectations.
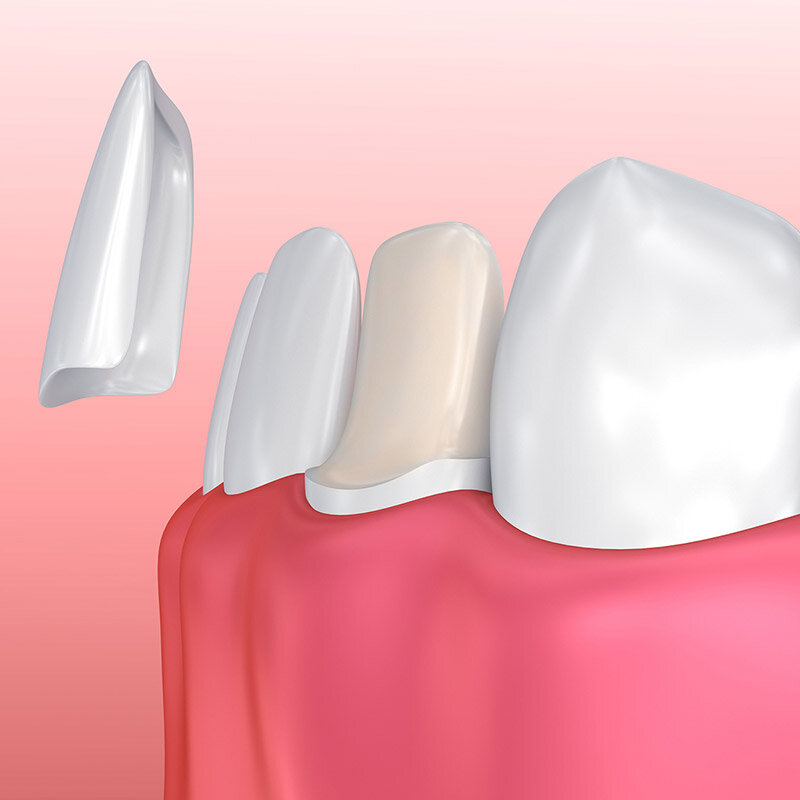
What is a dental veneer?
Dental veneer, a thin, tooth-coloured material, is used to improve the appearance of teeth. People generally describe it as a shell or coating that bonds to the front surface of the tooth.
What is the purpose of applying dental veneers?
The purpose of veneer applications is to address aesthetic issues such as discolouration, shape or size anomalies, and fractures in the teeth. At the same time, it aims to preserve the tooth structure and can help reduce periodontal and pulpal issues that more invasive methods might cause.
What are the types of dental veneers?
The types of dental veneers vary based on the material used, the application technique, and the area covered. The types of dental veneers are as follows:
According to the material used:
Porcelain Veneers:
People frequently prefer porcelain veneers because of their aesthetic appearance, colour stability, and durability. They are quite successful in mimicking the natural tooth structure.
Feldspathic porcelain veneers:
It is created by layering glass-based (silicon dioxide) powder and liquid materials. It exhibits high translucency (light permeability) similar to natural teeth.
Pressed ceramic veneers:
High temperatures melt it, then moulds press it into shape. (IPS Empress, OPC).
CAD/CAM ceramic veneers:
Manufactured from specially sintered ceramic blocks (zirconia, glass-bonded ceramic, or lithium disilicate) using milling technology (e.g., CEREC).
Composite Veneers:
Composite veneers are made from resin-based materials and are generally a more economical option.
According to the application technique:
Direct veneers:
Composite veneers are applied by the dentist by shaping them directly in the mouth.
Indirect veneers:
These are porcelain or composite veneers prepared in the laboratory by taking tooth impressions.
According to the veneer area:
Partial veneers:
These are veneers that cover only a part of the tooth. They are ideal for teeth with minor local discolouration or defects. It is less invasive and protects the tooth tissue more.
Full veneers:
These are veneers that cover the entire front surface of the tooth. They are used for teeth with more extensive discolouration, deformities, or damage.
Palatal Veneers:
These are veneers applied to the inner surface of the teeth. It is generally used in the treatment of tooth erosions.
Ultrathin veneers (Thineers, Lumineers):
Very thin (up to 0.3 mm) porcelain veneers. They require minimal tooth preparation or can be applied without any tooth cutting. They are suitable for mild discolouration or minor deformities.
Tooth Preparation:
Minimal preparation veneers:
These are veneers in which the tooth is only minimally abraded.
No-Prep veneers:
These are veneers in which the tooth is not abraded at all or very little abraded. Ultrathin veneers fall into this category.
Veneers with window preparation:
It is the most conservative type of preparation that protects the enamel in the incisal area.
Incisal-lapping veneers:
It is the preparation used when the tooth needs to be extended or when the damage in the incisal area requires restoration.
—–
What is the difference between porcelain veneer and traditional veneer?
The differences between porcelain veneers and traditional veneers are based on various factors such as the materials used, the production techniques, and the application methods. The term “traditional veneer” generally refers to veneers made of feldspathic porcelain, manually produced in a laboratory, while porcelain veneers encompass a wider range of materials and production techniques. Here are the main differences:
Material and manufacturing technique:
Traditional veneers are generally made from feldspathic porcelain. These types of porcelain are created by layering glass-based (silicon dioxide) powder and liquid materials. The production process is generally carried out manually in the laboratory, which means that the results may vary depending on the technician’s skill. Feldspathic porcelain exhibits high translucency (light permeability) similar to natural teeth. However, its mechanical properties are low and it is more prone to chipping.
Porcelain veneers can be made from various materials, including feldspathic porcelain, pressed ceramics, and CAD/CAM ceramics.
Durability and aesthetics:
Traditional veneers have a high ability to mimic the natural appearance of feldspathic porcelain, making it easy to achieve aesthetic results. However, due to their brittle structure, they should be used with caution, especially in areas where chewing forces are high. Porcelain veneers, different types of porcelain offer varying durability and aesthetic properties. For example, materials like lithium disilicate yield good results in both aesthetics and durability, while materials like zirconia provide higher durability. Veneers produced with CAD/CAM technology offer more precise and predictable results.
Application methods:
Traditional veneers, Since they are usually produced manually in the laboratory, the dentist takes measurements and sends them to the laboratory. Then, the fitting and bonding stages follow. Porcelain veneers can be produced using traditional methods, but thanks to CAD/CAM technology, they can also be applied in the same session.
Tooth Preparation:
Traditional veneers generally require minimal tooth preparation. However, due to the brittleness of feldspathic porcelain, in some cases, more dental tissue may need to be removed. Porcelain veneers can be applied with minimal tooth preparation, but in some cases, different types of preparations may be required.
Cost and duration
Traditional veneers can be more expensive and have a longer treatment process because they require a laboratory procedure. Porcelain veneers can vary in cost and duration depending on the materials and production techniques used. Those produced with CAD/CAM can be completed in the same session, while others may require laboratory time.
Front teeth:
Porcelain veneers give very good aesthetic results, especially on the front teeth (central and lateral incisors, canines).
Upper jaw teeth:
Maxillary anterior teeth are frequently preferred areas for porcelain veneer applications.
Porcelain dental veneers can be applied to teeth with various aesthetic and functional issues. The situations in which porcelain veneers can be applied are as follows:
Stained teeth:
Porcelain veneers are an ideal solution for teeth with permanent discolorations, such as tetracycline staining, that cannot be addressed by teeth whitening methods.
Teeth with deformities:
In the correction of teeth with congenital shape deformities, it is used in cases such as small teeth (microdontia), notched teeth (Hutchinson teeth), or conical teeth (peg lateral).
Spaced teeth (Diastema):
Porcelain veneers are an effective method for closing the gaps between the front teeth.
Broken or worn teeth:
Porcelain veneers can be used in the restoration of broken, cracked, or worn teeth.
Mild position disorders:
Porcelain veneers can be used in the correction of mild crowding and rotation of the teeth.
Size and length problems:
Porcelain veneers can be used to adjust the size and length of teeth, especially to lengthen short teeth.
Improvement of smile aesthetics:
In general, porcelain veneers can be preferred to improve smile aesthetics and achieve a more attractive smile.
- Patients with bruxism (teeth grinding) or parafunctional habits may cause breakage or damage to the veneers.
- Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum problems and caries formation around the veneers.
- Gum health is important for the success of veneers. Patients with active gum disease should first have this problem treated.
- There must be sufficient enamel tissue for the veneers to adhere to the tooth. Teeth with insufficient enamel tissue or teeth with too much restoration may not be suitable for veneers.
- Root canal-treated teeth may not have enough support for veneers, and full crowns may be more suitable.
- Orthodontic treatment may be more appropriate for correcting severely crowded teeth.
- Teeth that have lost more than one third of their tooth structure may not be suitable for veneers.
This process includes careful planning, preparation, and application stages. The stages of application of porcelain veneers on teeth are as follows:
Assessment and planning:
When you come to ViviMedi, our dentist will examine your teeth and smile in detail and evaluate the colour, shape, size, and position of your teeth and your existing aesthetic problems.
- Our dentist will create a special treatment plan for you, taking into account your expectations and the condition of your teeth. At this stage, he/she decides on which teeth to apply veneers, which type of veneers (direct or indirect), and which material to use.
- Photographs of the current condition of your teeth are taken, and a model is created by taking intraoral measurements.
- A model (mock-up) is prepared with the measurements taken, and how the veneers will look on this model is evaluated by our dentist together with you. This stage allows you to see the treatment result in advance.
- After the mock-up, the teeth are wax modelled (wax-up). This model is used to determine the final shape and dimensions of the veneers and is used as a reference during tooth cutting.
Preparation of your teeth:
- If necessary, your teeth will be numbed with local anaesthesia.
- The tooth surface is cleaned of plaque and other debris.
- A small amount of enamel is removed from the tooth surface for the placement of the veneers. This process varies according to the thickness of the veneer and the desired result. The enamel tissue is preserved, and as little tooth cutting is performed as possible. Enamel is removed at a depth of 0.3-0.5 mm or 0.4-0.7 mm on the front surface of the tooth.
- On the lateral surfaces of the teeth, a minimal preparation is made up to the contact points.
Laboratory Phase:
- Your dental impressions are sent to the laboratory. In the laboratory, porcelain veneers are prepared using these impressions. In the laboratory, veneers are produced using special techniques.
- The colour of the veneers is determined to be compatible with your tooth colour.
Rehearsal:
The prepared porcelain veneers are attached to your teeth, and their compatibility is evaluated. It is very important that the veneers fit the teeth perfectly, the edges are compatible with the gums, and there are no gaps. Then, the suitability of the proximal contact points is checked. If necessary, small corrections are made to the veneers.
Cementation:
The surface of your teeth is treated with acid (phosphoric acid) for roughening and cleaning. Then a bonding agent (dentin binder) is applied. The inner surface of the veneer is also roughened with a special acid (hydrofluoric acid), and silane is applied. These processes ensure better adhesion of the veneer to the tooth. The selected resin cement (luting cement) is applied to the inner surface of the veneer, and the veneer is placed on your tooth. The cement is hardened with a light device. Polymerisation time varies according to the type of cement. After hardening, glycerin is applied to the surface to remove the inhibition layer and complete the polymerisation.
Final checks and polishing:
The bite of your teeth is checked, and minor corrections are made if necessary. The surface of the veneers is polished to achieve a shine similar to natural teeth.
Maintenance and control:
Your porcelain veneers are now ready, and our dentist will inform and advise you on the things you should pay attention to for the longevity of the veneers.
Porcelain dental veneers, while frequently preferred as a treatment method in aesthetic dentistry, have both advantages and disadvantages. These advantages and disadvantages are as follows:
Advantages:
- Porcelain veneers offer an extremely natural and aesthetic appearance thanks to their ability to mimic the light transmission and reflection of natural tooth enamel. This is a great advantage to meet aesthetic expectations, especially in the front teeth. Both intrinsic and superficial stains can be controlled with porcelain, and a vivid appearance is achieved thanks to natural fluorescence.
- Porcelain veneers can effectively correct tooth discolouration, deformities, gaps, and slight misalignments. They give more successful results than bleaching methods, especially in the removal of permanent stains such as tetracycline. They also provide a more proportional smile by adjusting the size and length of the teeth.
- Since porcelain veneers are applied as a thin layer on the teeth, they are prepared with minimal loss of material from the tooth structure. This provides a more conservative treatment by preserving the natural structure of the teeth. In some cases, applications can even be made without cutting any teeth.
- With good oral hygiene and regular care, porcelain veneers can maintain their durability and aesthetic appearance for many years. Their durability increases, especially when they adhere well to the enamel tissue.
- Porcelain is a biocompatible material that does not harm gum health. Therefore, it does not cause gum irritation and provides long-term success.
- Porcelain is more resistant to liquid absorption than other coating materials. Thus, it is more resistant to staining.
- Small cracks, fractures, abrasions, and developmental disorders can be corrected with porcelain veneers.
- Factors such as the shape, size, position, and colour of the teeth can be adjusted with veneers to create a personalised smile design.
- In porcelain veneer applications, a small amount of material is removed from the teeth, which provides an advantage in terms of dental health by preserving the natural structure of the teeth.
- Although it requires a laboratory phase compared to direct composite veneers, porcelain veneers can generally be completed in a short time and with few appointments.
Disadvantages:
- Porcelain veneers require at least two appointments because they require a laboratory phase. This may be a disadvantage for some patients.
- Porcelain veneers are more costly than direct composite restorations because they require a laboratory phase and additional clinical time.
- Porcelain veneers cannot be repaired in case of cracks or fractures and usually need to be replaced. This is a disadvantage compared to direct composite veneers.
- Temporary sensitivity may be observed in some patients due to tooth cutting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Ceramic veneers can be applied to a single tooth, to all front teeth, or to a larger number of teeth. Treatment planning varies depending on many factors, such as the needs of the patient, the condition of the teeth, occlusion, cost, and time. The important thing is that the dentist and the patient make a joint decision and create a personalised treatment plan.
Although ceramic dental veneers are generally used for aesthetic purposes on anterior teeth, in some cases they can also be applied to molars. The applicability of veneers on molars varies depending on case-specific conditions and treatment goals.
Although porcelain veneers are an effective solution for the correction of small fractures and other aesthetic problems, they may not always be suitable for very large fractures in the teeth. In such cases, more extensive restorations such as crowns or onlays may be preferred.
The durability of porcelain dental veneers depends on many factors and usually has a lifespan between 10 and 15 years. However, with proper care and attention, this can be extended.
What to do when porcelain veneers are fractured may vary depending on the cause of the fracture, its size, and the aesthetic problem it creates. In case of a fracture in porcelain veneers, it is important to first consult a dentist and get a professional evaluation. Depending on the size and cause of the fracture, the veneer may need to be repaired or replaced. In addition, appropriate precautions should be taken to prevent fractures from recurring, and regular dental check-ups should not be neglected.
The price of porcelain dental veneers varies between 150 and 280 euros depending on the selected clinic, the material used, and the scope of treatment. Since prices may vary depending on the city where the clinic is located, the experience of the dentist, and your treatment plan, it is recommended that you contact our clinic, ViviMedi, directly to get information about the current price.

