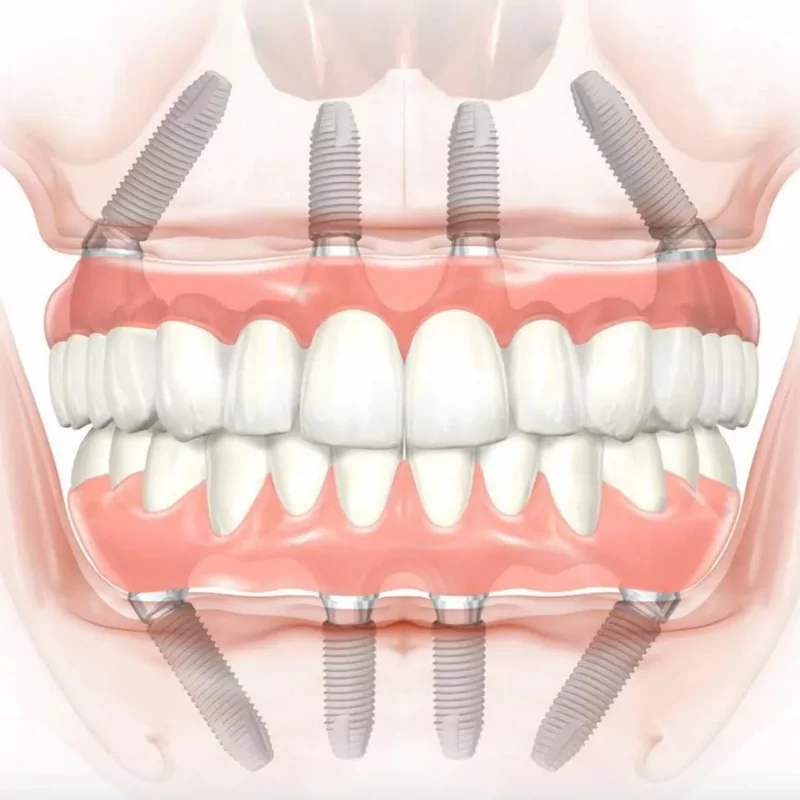
Dental implants have become a cornerstone in restorative dentistry, not only for their ability to replace missing teeth but also for their significant role in maintaining and preserving jawbone health. Understanding how dental implants contribute to bone health is crucial for appreciating their long-term benefits.
The Impact of Tooth Loss on Jawbone Health
When a tooth is lost, the underlying jawbone loses its primary source of stimulation: the natural forces exerted during chewing. This lack of stimulation can lead to a process called bone resorption, where the bone gradually deteriorates and loses density. Bone resorption has several detrimental effects:
Reduction in Bone Volume: The jawbone shrinks, which can alter facial structure, leading to a sunken appearance and premature aging.
Compromised Stability for Adjacent Teeth: The loss of bone can affect the stability of neighboring teeth, increasing the risk of further tooth loss.
Difficulty in Future Restorations: Reduced bone volume can complicate future dental restorations, such as implants or bridges, often necessitating additional procedures like bone grafting.
How Dental Implants Preserve Jawbone Health?
Dental implants play a pivotal role in preventing bone resorption and preserving jaw structure. Here’s how they achieve this:
Osseointegration: Dental implants are typically made of titanium or zirconia, materials that are biocompatible and integrate well with the bone. This process, known as osseointegration, involves the bone growing around and fusing with the implant, providing a stable and secure anchor much like a natural tooth root.
Stimulation of Bone Growth: Implants mimic the natural tooth roots, stimulating the jawbone through the forces exerted during chewing and biting. This stimulation is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing resorption.
Maintaining Facial Structure: By preserving bone volume, dental implants help maintain the natural contours of the face. This prevents the sunken appearance often associated with prolonged tooth loss and helps in maintaining a youthful look.
Support for Adjacent Teeth: Implants provide stability for neighboring teeth, preventing them from shifting into the gap left by a missing tooth. This helps maintain the overall alignment and health of the dental arch.
Bone Grafting and Augmentation for Implant Success
In cases where significant bone loss has already occurred, bone grafting procedures can enhance the success of dental implants. Bone grafting involves adding bone or bone-like materials to the jaw, promoting new bone growth and providing a stable foundation for implants. There are various types of bone grafts:
Autografts: Bone taken from another part of the patient’s body, such as the hip or another area of the jaw.
Allografts: Bone sourced from a donor.
Xenografts: Bone derived from animal sources, typically bovine.
Synthetic Grafts: Man-made materials that stimulate bone growth.
Innovations Enhancing Bone Health with Dental Implants
Growth Factors: The use of growth factors such as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) can enhance bone regeneration and healing around the implant site.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): These are derived from the patient’s own blood and are rich in growth factors that accelerate healing and bone growth.
Nanotechnology: Implants with nanoscale surface modifications promote better bone integration and faster healing by increasing the surface area for bone cells to attach and grow.
Long-Term Benefits of Dental Implants for Bone Health
Durability and Stability: Dental implants provide a long-term solution that maintains bone health and prevents the progressive bone loss associated with dentures or missing teeth.
Enhanced Oral Function: By preserving bone structure, implants support natural chewing forces, which are essential for maintaining bone health and overall oral function.
Improved Aesthetics and Confidence: Maintaining bone volume helps preserve facial aesthetics, leading to improved self-confidence and quality of life.
Conclusion
Dental implants are not just a solution for missing teeth; they are a critical component in maintaining jawbone health and preserving facial structure. Through the process of osseointegration and the stimulation of bone growth, implants help prevent bone resorption, support adjacent teeth, and maintain the natural contours of the face. Advances in technology, such as growth factors and nanotechnology, continue to enhance the success and benefits of dental implants, making them an indispensable tool in modern dentistry for ensuring long-term oral health and overall well-being.